The Cost of Cybersecurity Failures in 2025
The much-anticipated IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report for 2025 has arrived, and it paints a fascinating picture of our evolving cybersecurity landscape. While there's good news on some fronts, the findings on artificial intelligence security gaps should set alarm bells ringing for organisations of all sizes.
At EJN Labs, we've combed through the report to bring you the most crucial takeaways and, more importantly, what they mean for your security posture in today's AI-driven world.
Global Trends: A Mixed Bag of Results
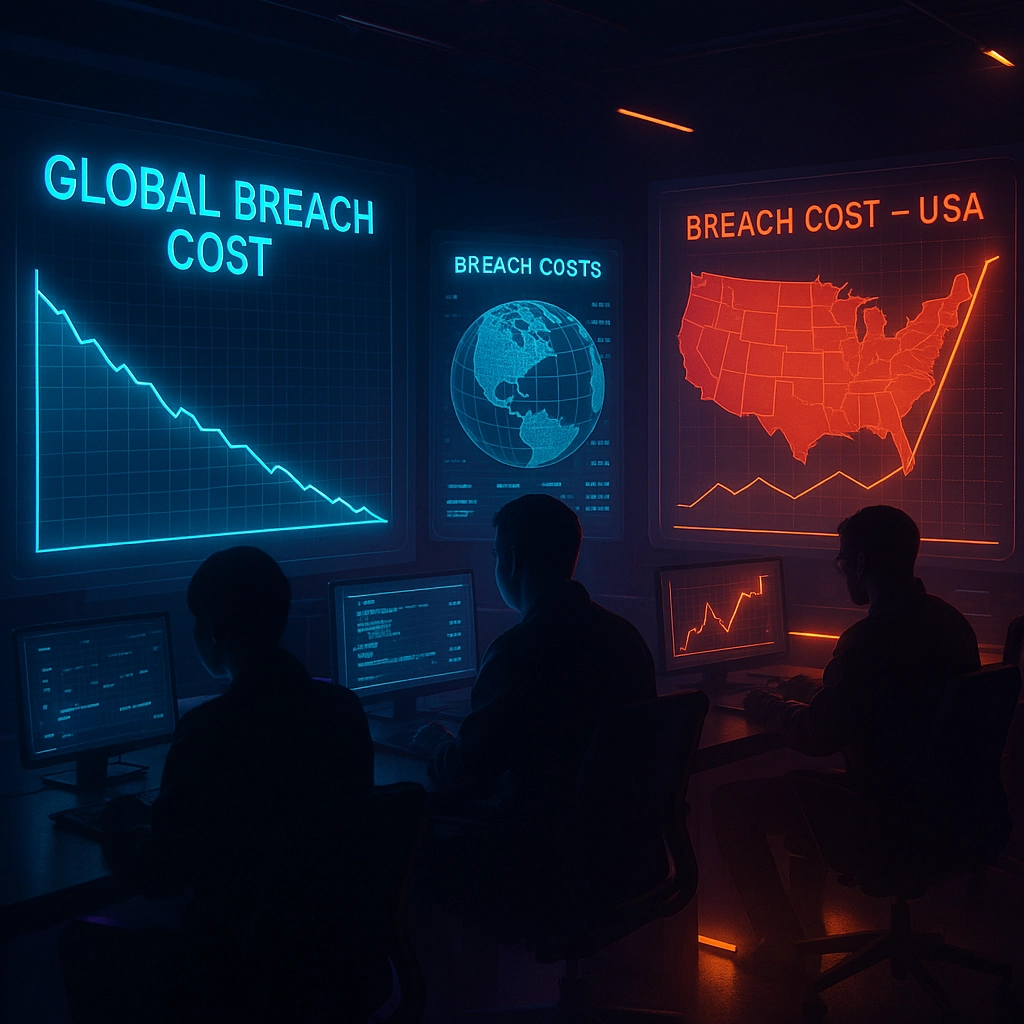
For the first time in years, there's some positive news on the global front. The worldwide average cost of a data breach has fallen to £4.44 million, down 9% from £4.88 million in 2024. This decrease represents a return to 2023 levels and suggests that certain cybersecurity measures are bearing fruit.
What's driving this improvement? According to the report, organisations deploying AI and automation tools for threat detection and response are seeing significantly faster containment times, which directly translates to lower costs.
However, this global decrease masks a troubling outlier: the United States. In the US, breach costs have climbed to a record £10.22 million, up from £9.36 million last year. This stark regional difference highlights how varying regulatory environments, litigation costs, and attack sophistication can dramatically impact the financial toll of cybersecurity incidents.

The AI Security Paradox: Rapid Adoption, Lagging Protection
Perhaps the most concerning finding from this year's report is what we might call the "AI security paradox." While organisations are rapidly embracing artificial intelligence to transform their operations, they're neglecting to secure these same systems with equal rigour.
The numbers tell a startling story:
- 13% of organisations reported breaches involving their AI models or applications
- A staggering 97% of these breaches occurred in systems lacking basic access controls
- 60% of AI-related breaches led to compromised data
- 31% resulted in operational disruptions, including workflow halts and financial losses
- 8% of companies admitted they weren't even sure if their AI systems had been compromised
As Suja Viswesan, IBM Security's CTO, notes in the report: "We're witnessing a concerning gap between the pace of AI adoption and the implementation of proper security oversight. Organisations are rightfully excited about AI's transformative potential, but many are failing to apply established security principles to these new technologies."
The Shadow AI Problem
One particularly troubling trend identified in the report is the rise of "shadow AI" – the unauthorised use of AI tools and platforms within organisations. Much like the shadow IT problem of previous years, shadow AI introduces significant security risks that bypass corporate governance structures.
When employees use unapproved AI systems to process sensitive data, they may inadvertently expose proprietary information, customer details, or intellectual property. What makes this especially dangerous is that AI models themselves become high-value targets – as they contain concentrated repositories of an organisation's most valuable data.
The report found that many organisations lack visibility into where and how AI is being used across their operations. This blind spot creates perfect conditions for security gaps that sophisticated attackers are increasingly equipped to exploit.
The Real-World Impact of Breaches
Beyond the immediate financial costs, the IBM report highlights several concerning downstream effects of data breaches:
Extended Recovery Timelines
Most organisations took more than 100 days to fully recover from breaches, with the average time to identify and contain a breach hovering around 200 days. This extended timeline means prolonged exposure, higher costs, and longer periods of operational disruption.
Consumer Cost Pass-Through
Perhaps most troubling for the broader economy, 48% of organisations raised their product or service prices as a direct result of suffering a breach. Among these, 30% implemented price increases exceeding 15%. This suggests that the true cost of inadequate cybersecurity is ultimately borne by consumers and clients.

The AI Security Gap: Why It Exists and Why It Matters
To understand why AI systems are particularly vulnerable, we need to recognise several factors unique to this technology:
1. Accelerated Deployment
The competitive pressure to implement AI capabilities has led many organisations to prioritise speed over security. The result is often AI systems deployed without the rigorous security assessments applied to traditional IT infrastructure.
2. Unique Attack Surfaces
AI systems present novel attack vectors that traditional security approaches might miss. These include:
- Model poisoning: Where attackers manipulate training data to corrupt AI outputs
- Prompt injection: Where malicious inputs cause AI systems to behave in unintended ways
- Data extraction: Where techniques like "jailbreaking" allow attackers to extract sensitive information from AI models
3. Governance Challenges
The cross-functional nature of AI deployments often creates confusion about security ownership. Is it the data science team's responsibility? IT security? Compliance? This ambiguity creates gaps that attackers can exploit.
4. The Black Box Problem
Many AI systems function as "black boxes" where decision processes aren't fully transparent. This opacity makes it difficult to identify when systems have been compromised or are behaving abnormally.
Five Essential Steps to Strengthen Your AI Security Posture
Based on the IBM report findings and our experience at EJN Labs, here are five critical steps every organisation should take to address AI security gaps:
1. Implement Robust AI Governance
Establish clear policies and procedures for AI adoption, development, and deployment. This includes:
- Formal approval processes for new AI initiatives
- Clear security requirements for AI vendors and tools
- Designated security ownership for AI systems
- Regular security assessments of AI applications
2. Apply Zero Trust Principles to AI
Treat AI systems like any other critical infrastructure by implementing zero trust security principles:
- Require authentication for all AI system access
- Implement least-privilege access controls
- Encrypt sensitive data used in AI training and inference
- Monitor AI system behaviour for anomalies
To learn more about implementing effective penetration testing as part of your security strategy, visit our guide on what pentesting is and why you need it.
3. Conduct AI-Specific Risk Assessments
Standard security assessments may miss AI-specific vulnerabilities. Conduct specialised assessments that consider:
- Training data integrity and security
- Model vulnerabilities and attack surfaces
- Prompt injection and jailbreaking attempts
- Compliance with AI-specific regulations
4. Address Shadow AI
Take proactive steps to identify and manage unauthorised AI use:
- Audit your environment for unapproved AI tools
- Provide approved alternatives for common AI use cases
- Educate employees about AI security risks
- Implement data loss prevention tools configured for AI contexts
5. Prepare for AI Breaches
Include AI systems in your incident response planning:
- Develop specific playbooks for AI-related incidents
- Train response teams on AI system architecture
- Establish containment procedures for compromised AI models
- Implement backup systems for AI-dependent operations

The Technological Divide: AI Security Haves and Have-Nots
One of the more subtle but important findings in the IBM report is the emerging technological divide between organisations. Those with mature AI security practices experienced breach costs approximately 30% lower than those without such practices.
This suggests we're entering an era where cybersecurity capability may create significant competitive advantages. Organisations that can secure their AI investments will likely see better outcomes in several dimensions:
- Lower incident-related costs
- Greater customer trust and retention
- Ability to deploy AI more broadly without elevated risk
- Reduced regulatory exposure in an increasingly regulated AI landscape
Conclusion: The Path Forward
The 2025 IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report sends a clear message: while we're making progress in some areas of cybersecurity, the rapid adoption of AI has created new vulnerabilities that many organisations are ill-equipped to address.
The good news is that established security principles still apply. By extending existing best practices to AI systems and addressing AI-specific risks, organisations can significantly reduce their exposure.
At EJN Labs, we specialise in helping organisations identify and address security vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. Our penetration testing services include AI system assessment and can help you understand where your greatest risks lie.
The AI revolution offers tremendous potential for innovation and efficiency, but only if we can secure it properly. As we move forward, bridging the gap between AI adoption and AI security must be a top priority for every organisation that values its data, operations, and reputation.
For more information on how to protect your systems from emerging threats, explore our articles on cybersecurity or contact us to discuss your specific security needs.









Leave a Reply