The cybersecurity landscape has entered a new era where artificial intelligence is not just defending systems but actively powering sophisticated attacks. Recent WhatsApp zero-click vulnerabilities and emerging threats like HexStrike represent a fundamental shift in how malware operates, requiring no user interaction whilst leveraging AI to maximise damage.
With over 90 high-profile individuals recently targeted through WhatsApp zero-click attacks, including journalists and activists, the question is not whether your organisation will encounter AI-powered threats, but when.
What Makes Zero-Click Attacks So Dangerous?
Zero-click attacks represent the pinnacle of malware sophistication. Unlike traditional attacks that require users to click malicious links or download infected files, these exploits compromise devices completely silently, without any victim interaction whatsoever.
The recent WhatsApp campaign demonstrates this perfectly. Attackers exploited CVE-2025-55177, a flaw in WhatsApp's linked device synchronisation protocol, combined with iOS vulnerability CVE-2025-4300 to achieve remote code execution. The attack chain required absolutely no action from victims, making it virtually undetectable until after compromise.

What makes these attacks particularly concerning is their forensic invisibility. Traditional malware leaves digital breadcrumbs through user interactions, but zero-click exploits operate in the shadows, leaving minimal traces for security teams to investigate. This combination of stealth and automation makes them ideal vehicles for AI-enhanced capabilities.
The WhatsApp Zero-Click Campaign: A Case Study
The recent WhatsApp attack campaign, attributed to Israeli surveillance firm Paragon Solutions and their "Graphite" spyware, targeted over 90 individuals across multiple countries. The attack specifically focused on journalists, activists, and civil society members, suggesting state-sponsored or politically motivated objectives.
The technical sophistication is remarkable. By exploiting the linked device synchronisation protocol, attackers could gain initial access, then leverage additional vulnerabilities to achieve full device compromise. The attack worked across WhatsApp for iOS prior to version 2.25.21.73, WhatsApp Business for iOS, and WhatsApp for Mac prior to version 2.25.21.78.
Despite receiving only a medium severity rating with a CVSS score of 5.4, the vulnerability becomes exponentially more dangerous when chained with other exploits. This demonstrates how modern attackers combine multiple seemingly minor flaws to create devastating attack chains.
CISA added this vulnerability to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog on 2nd September 2025, confirming active exploitation in the wild. The speed of exploitation following discovery highlights how quickly sophisticated actors can weaponise new vulnerabilities.
AI's Role in Modern Malware Evolution
Artificial intelligence is fundamentally changing how malware operates, making attacks more targeted, persistent, and difficult to detect. AI-powered malware can adapt its behaviour based on the target environment, learning from defensive measures and evolving to bypass security controls.

Traditional signature-based detection becomes largely ineffective against AI-enhanced threats. These systems can modify their code signatures dynamically, generate polymorphic variations, and even learn from attempted detections to improve future attacks. The result is malware that becomes more sophisticated with each deployment.
AI also enables precision targeting at unprecedented scale. Rather than casting wide nets hoping for random victims, AI-powered malware can analyse vast datasets to identify high-value targets, customise attack vectors for specific environments, and optimise payload delivery for maximum impact.
The HexStrike Phenomenon
HexStrike represents a new category of AI-powered malware that combines multiple attack vectors with machine learning capabilities. While specific technical details remain limited as security researchers continue analysis, early indicators suggest it leverages AI for both target selection and attack customisation.
The malware reportedly uses natural language processing to analyse compromised communications, identifying additional targets and attack opportunities from email content, messaging apps, and document repositories. This creates a self-propagating attack that grows more effective as it spreads.
What makes HexStrike particularly concerning is its apparent ability to remain dormant until optimal conditions are met. Rather than immediately executing payloads, it can lie dormant for weeks or months, gathering intelligence and waiting for the perfect moment to strike.
Network Protocol Vulnerabilities
Modern AI-powered attacks increasingly target network protocols themselves rather than just applications. By infiltrating networks and exploiting communication protocol vulnerabilities, attackers gain deeper access with broader permissions.
This approach is particularly effective because network protocols are often overlooked in security assessments. Organisations focus heavily on application security whilst leaving fundamental communication mechanisms relatively unexamined. AI enhances this attack vector by automating protocol analysis and identifying subtle vulnerabilities that human attackers might miss.
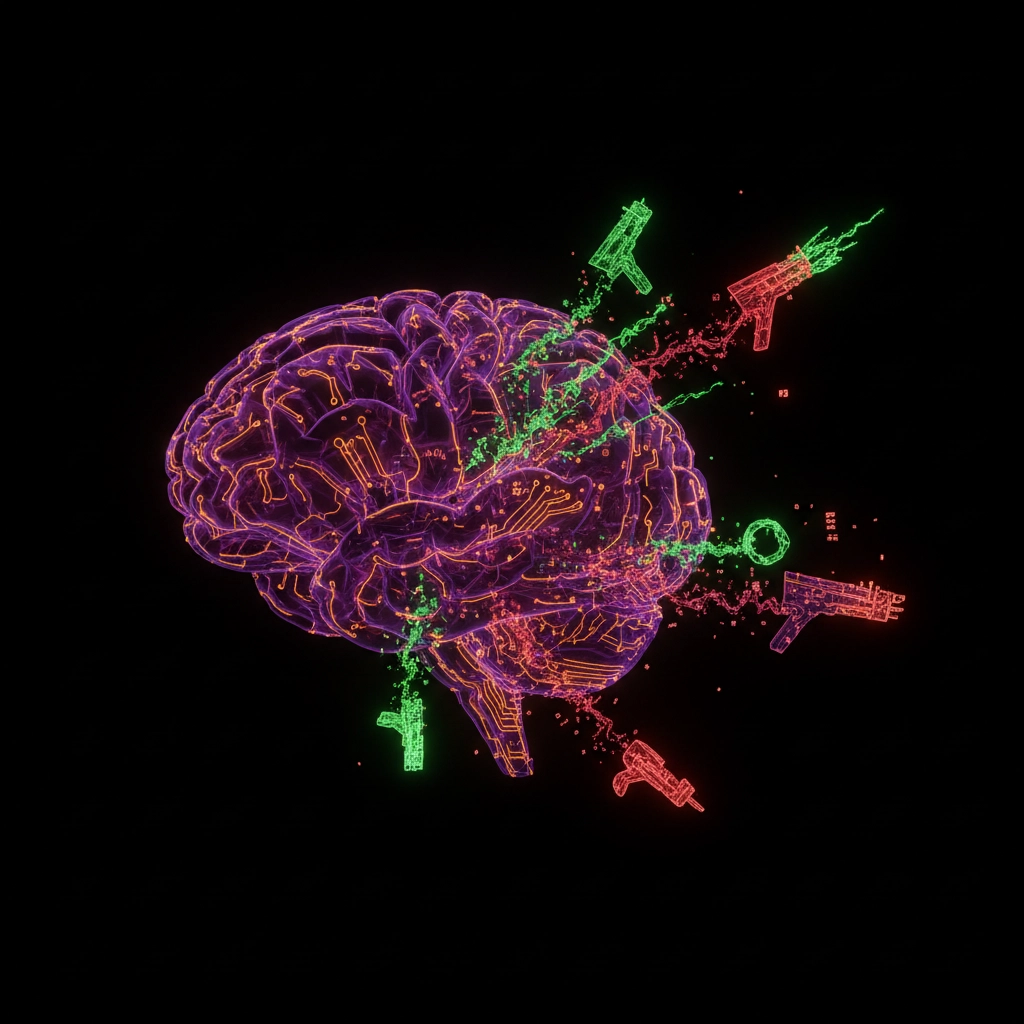
The weaponisation of popular applications represents another concerning trend. Rather than creating standalone malware, attackers inject malicious code into legitimate applications, allowing malware to spread silently within established digital ecosystems. AI accelerates this process by automatically identifying suitable applications and optimal injection points.
Business Impact and Risk Assessment
For UK businesses, these developments represent significant risk escalation. AI-powered malware can cause devastating data breaches, deploy ransomware with surgical precision, and enable long-term corporate espionage. State-sponsored actors and corporate rivals increasingly deploy these tools for covert surveillance and competitive intelligence gathering.
The financial implications extend beyond immediate breach costs. AI-powered attacks can remain undetected for months, continuously exfiltrating sensitive data whilst mapping internal networks for future attacks. When discovered, the scope of compromise is often far broader than initially apparent.
Regulatory compliance becomes more challenging as well. With GDPR and other privacy regulations requiring organisations to detect and report breaches promptly, the stealth capabilities of AI-powered malware create significant compliance risks. Organisations may unknowingly operate in breach of regulations for extended periods.
Protection Strategies for Modern Threats
Defending against AI-powered malware requires fundamental changes to security strategy. Traditional reactive approaches prove insufficient against threats that learn and adapt faster than human defenders can respond.
Immediate actions include ensuring all WhatsApp installations are updated to the latest versions across all devices. iOS devices must also be updated to address CVE-2025-4300. However, patching alone is insufficient against AI-powered threats that continuously evolve.
Implementing robust endpoint detection and response solutions becomes critical. These systems must incorporate AI capabilities themselves to match the sophistication of modern threats. Traditional signature-based antivirus simply cannot keep pace with polymorphic, AI-enhanced malware.

Network monitoring requires significant enhancement as well. Organisations need solutions capable of identifying subtle protocol anomalies and unusual communication patterns that might indicate AI-powered reconnaissance or data exfiltration.
Regular security assessments must evolve beyond traditional penetration testing approaches. Modern threats require continuous monitoring and testing that can identify vulnerabilities before AI-powered attacks exploit them.
The Future of Cyber Threats
The convergence of artificial intelligence and malware development represents a permanent shift in the threat landscape. Attacks will continue becoming more sophisticated, targeted, and difficult to detect. Organisations that fail to adapt their security strategies accordingly face exponentially increasing risk.
Zero-click attacks will likely expand beyond messaging applications to target other communication platforms and protocols. As AI capabilities improve, we can expect attacks that require even less interaction whilst achieving greater compromise scope.
The democratisation of AI tools also means sophisticated attack capabilities will become available to less skilled threat actors. What once required nation-state resources may soon be achievable by smaller criminal groups, dramatically expanding the threat actor pool.
For organisations seeking to navigate this evolving landscape, partnering with cybersecurity specialists who understand AI-powered threats becomes essential. The complexity of modern attacks exceeds what most internal teams can handle alone.
Contact EJN Labs today to discuss how we can help protect your organisation against the next generation of cyber threats. The question is not whether AI-powered attacks will target your business, but whether you will be prepared when they do.









Leave a Reply