The Growing Challenge of Authorization Sprawl
In today's cloud-first world, businesses are embracing SaaS solutions at an unprecedented rate. The average enterprise now uses over 130 different SaaS applications, with larger organizations often deploying 200+ cloud services across departments. But this explosive growth comes with a shadow side: authorization sprawl.
Authorization sprawl occurs when access permissions multiply across numerous applications without centralized oversight, creating a tangled web of who can access what. This phenomenon isn't just an IT management headache—it's a significant security vulnerability that organizations can no longer afford to ignore.
What Exactly Is Authorization Sprawl?
Authorization sprawl manifests when:
- Multiple users have excessive permissions across numerous applications
- Access rights remain active long after they're needed
- Different departments create siloed permission structures
- IT loses visibility into who has access to what data
- Offboarding processes fail to revoke all access points
The result? A chaotic environment where the principle of least privilege is abandoned, and security gaps widen daily.

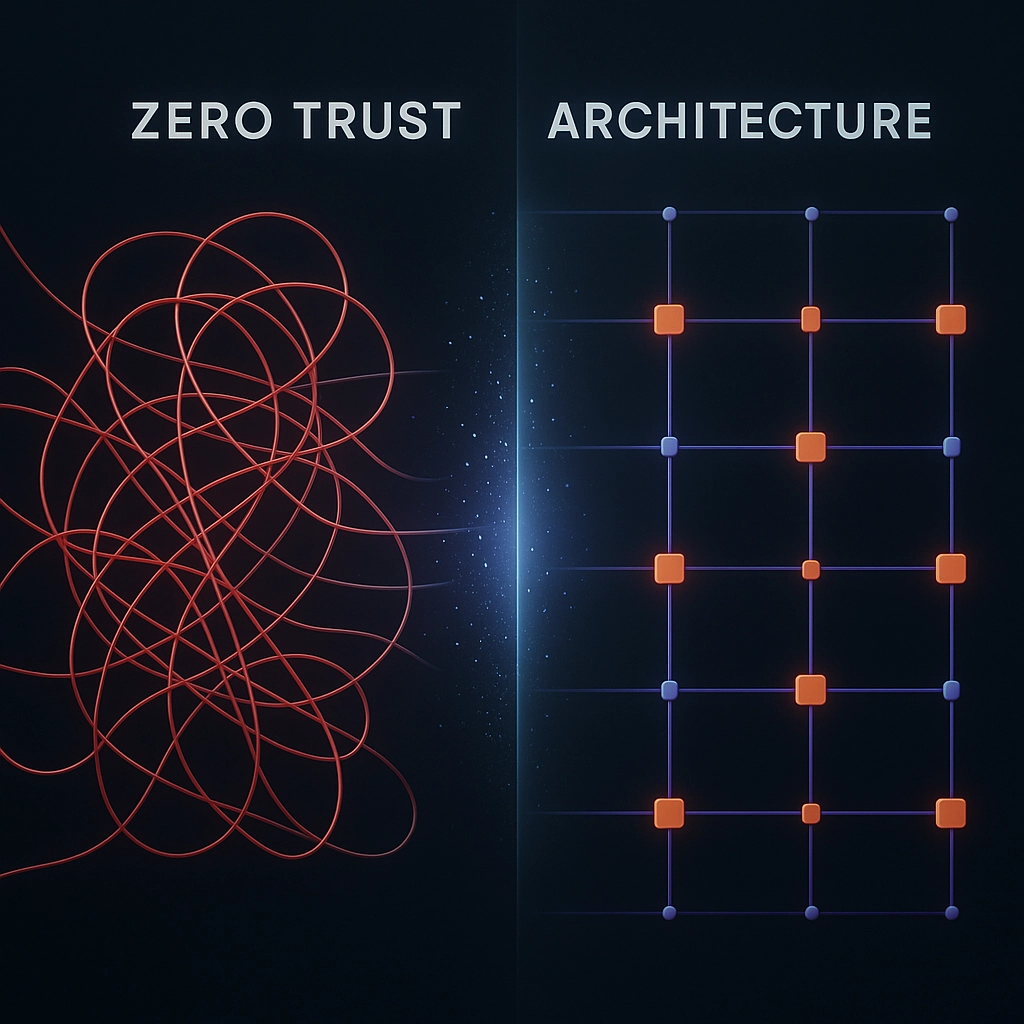
Zero Trust: The Framework for Modern SaaS Security
Zero Trust isn't just another cybersecurity buzzword—it's a paradigm shift that directly addresses the challenges of authorization sprawl. At its core, Zero Trust operates on a simple principle: "never trust, always verify." This framework assumes that threats exist both outside and inside the network, requiring continuous verification of every user and device.
For SaaS environments specifically, Zero Trust rejects the traditional security model where authentication happens once at login. Instead, it introduces continuous validation throughout the user journey.
Key Zero Trust Principles for SaaS Security:
- Identity-Based Security: Authentication revolves around user identity rather than network location
- Least Privilege Access: Users receive only the minimum permissions necessary
- Micro-Segmentation: Applications and data stores are isolated with distinct access controls
- Continuous Verification: Access is continuously evaluated, not granted once and forgotten
- Risk-Based Conditional Access: Authentication requirements adjust based on risk signals
The Perfect Storm: Why SaaS Makes Authorization Management Difficult
SaaS environments present unique challenges for authorization management:
Decentralized Procurement
Marketing, HR, Sales, and other departments independently adopt SaaS solutions, creating identity silos that IT security teams struggle to track.
API Interconnectivity
Modern SaaS apps connect via APIs, propagating access rights across application boundaries. When a user has excessive permissions in one system, those privileges can cascade across interconnected services.
Rapid Evolution
SaaS platforms update features and permission structures frequently, sometimes deprecating previous access controls or introducing new permission types without warning.
Identity Fragmentation
Without centralized identity management, users accumulate multiple accounts across services, leading to inconsistent permission structures.

Implementing Zero Trust to Tame Authorization Sprawl
Successfully addressing authorization sprawl requires a strategic approach that combines technology, processes, and cultural shifts. Here's how to implement an effective Zero Trust framework:
1. Conduct a SaaS Authorization Audit
Before implementing Zero Trust, you need visibility into your current state:
- Discovery: Identify all SaaS applications in use across the organization
- Permission Mapping: Document who has access to what and why
- Risk Assessment: Evaluate which applications contain sensitive data
- Dependency Analysis: Map integrations between applications
2. Implement Centralized Identity and Access Management (IAM)
A robust IAM system serves as the foundation for Zero Trust in SaaS environments:
- Single Sign-On (SSO): Consolidate authentication through a central identity provider
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Require additional verification for all SaaS access
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Define standardized roles across applications
- Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC): Use contextual attributes to make dynamic access decisions
3. Adopt Just-in-Time (JIT) Access Principles
JIT access dramatically reduces standing privileges:
- Temporary Elevation: Grant heightened permissions only when needed and automatically revoke them
- Access Requests: Implement approval workflows for privilege escalation
- Session Time Limits: Enforce automatic timeouts on elevated access
- Activity Logging: Record all actions taken during privileged sessions
4. Deploy Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs)
CASBs serve as security enforcement points between users and cloud services:
- Visibility: Gain insights into shadow IT and unsanctioned app usage
- Data Loss Prevention: Control sensitive information flowing to and from SaaS applications
- Threat Protection: Identify malicious activities within SaaS environments
- Compliance Monitoring: Ensure SaaS usage aligns with regulatory requirements
5. Implement Continuous Monitoring and Automated Remediation
Zero Trust requires ongoing vigilance:
- User Behavior Analytics: Establish baselines for normal behavior
- Anomaly Detection: Flag unusual access patterns or data movements
- Automated Response: Revoke access when suspicious activities occur
- Regular Access Reviews: Schedule periodic certification of permissions
Real-World Example: Transforming SaaS Security at a Financial Services Firm
A mid-sized financial services company with 2,000 employees found itself struggling with SaaS sprawl across 175+ applications. During a security audit, they discovered:
- 37% of users had unnecessary admin privileges in at least one application
- 112 former employees still had active accounts in various SaaS platforms
- 42% of SaaS applications were connected to other services, creating permission cascades
- Sensitive financial data was accessible by non-finance personnel through integrated apps
The Zero Trust Transformation:
The company implemented a comprehensive Zero Trust approach:
- Consolidated Identity Management: Deployed a unified IAM platform with SSO across all SaaS applications
- Permission Rightsizing: Reduced admin accounts by 92% through proper role definition
- Access Lifecycle Management: Automated provisioning and deprovisioning tied to HR systems
- Conditional Access Policies: Implemented risk-based authentication requirements based on data sensitivity
- Continuous Monitoring: Deployed a CASB solution for ongoing visibility and control
Results:
Within six months, the company:
- Reduced their attack surface by 78%
- Decreased access-related security incidents by 65%
- Improved compliance posture for GDPR and PCI-DSS
- Streamlined user experience through consistent authentication flows
Best Practices for Maintaining Zero Trust in SaaS Environments
Even after implementing Zero Trust, maintaining it requires ongoing effort:
Regular Security Posture Assessments
Schedule quarterly reviews of your SaaS security posture, including permission structures, integrations, and access patterns.
Automated Lifecycle Management
Ensure that access provisioning and deprovisioning happen automatically when employees join, change roles, or leave.
Continuous Employee Education
Train users on security best practices and why access restrictions are essential.
API Security Focus
Pay special attention to API connections between applications, as these often become vectors for privilege escalation.
SaaS Vendor Management
Include security and access control capabilities in vendor selection criteria and regularly review their security practices.
Conclusion: Beyond Authorization Sprawl
As organizations increasingly depend on SaaS for critical business functions, authorization sprawl presents a growing security risk. Zero Trust principles offer a strategic framework to address this challenge by focusing on identity-centric security, continuous verification, and least privilege access.
By implementing centralized identity management, just-in-time access, and continuous monitoring, organizations can maintain security without sacrificing the agility and innovation that SaaS platforms enable.
At EJN Labs, we help organizations implement robust Zero Trust frameworks tailored to their specific SaaS environments. Our cloud security review services for AWS, Azure, and GCP help identify authorization gaps and implement effective remediation strategies.
The journey to Zero Trust is continuous, but the benefits—improved security posture, reduced risk, enhanced compliance, and better user experiences—make it well worth the investment.









Leave a Reply